Magnetic Bead-based Isolation Of Exosomes
The magnetic bead-based isolation workflow is dramatically shortened both by omitting the pre-enrichment step and providing an option for a very short capture time. Many receptors and proteins are found on the exosomal membrane.
 A Perspective On The Isolation And Characterization Of Extracellular Vesicles From Different Biofluids Rsc Advances Rsc Publishing
A Perspective On The Isolation And Characterization Of Extracellular Vesicles From Different Biofluids Rsc Advances Rsc Publishing
See more ideas about Magnetic bead-based isolation of exosomes

Also exosomes of tumor origin were isolated from tumor cells using antibodies against tumor-associated HER2 and EpCAM.. 80 Based on the specific surface markers of exosomes exosomes can be adsorbed and isolated after they are incubated with magnetic beads coated with corresponding antibodies Figure 3D. Magnetic beads are versatile tools for exosome isolation and downstream analysis. And kit for exosome detection and characterization from supernatants of cell cultures and biological fluids by flow cytometry.
Isolated bead-exosome complexes can be analyzed by flow cytometry Western blotting and electron microscopy. Thus magnetic separation with magnetic particles is a better approach as an alternative to latex beads for exosome capture which can isolate a more homogenous population of vesicles in terms of size morphology and protein content. Magnetic bead-based isolation of exosomes.
A magnet was used to attract the EVs-captured PLL-beads from the mixing solution. 1 Specific and Direct 2 Semi Generic and Direct and 3 Generic and Direct as well as exosome release from the magnetic beads. The process involves utilizing magnetic beads coated with capture molecules.
Magnetic beads offer a fast gent-le means of exosome isolation for proteomic analyses and RNA profiling among other uses. The present results confirmed the isolation of exosomes through analyses of size distribution morphology surface and internal protein markers and exosomal RNA. This method is based on the use of magnetic beads coated with antibodies against tetraspanin CD63 a common marker of exosomes which allows exosome detection in.
Developed a rapid and versatile technique for exosome isolation. Exosomes are here defined as extracellular vesicles EVs in the approximate size range of 30-100 nm in diameter and are observed in most body fluids containing typical exosomal markers such as CD9 CD63 and CD81. The process involves utilizing magnetic beads coated with capture molecules that recognize EV surface markers such as CD63.
Exosomes are here defined as extracellular vesicles EVs in the approximate size range of 30-100 nm in diameter and are observed in most body fluids containing typical exosomal markers such as CD9 CD63 and CD81. They are involved in multiple biological functions. Three direct exosome isolation strategies are described.
Magnetic bead-based exosome detection. Magnetic beads are versatile tools for exosome isolation and downstream analysis. Exosomes are here defined as extracellular vesicles EVs in the approximate size range of 30-100 nm in diameter and are observed in most body fluids containing typical exosomal markers such as CD9 CD63 and CD81.
We have thus designed a two-step magnetic bead-based 2MBB method for isolation a subset of EVs as well as their microRNAs from samples of a limited amount. Potential subpopulations of exosomes can be captured by targeting these markers using magnetic beads. Antibody-coated magnetic beads were effectively used to isolate exosomes from antigen presenting cells.
This characteristic is beneficial for the development of targeted techniques for exosome isolation by leveraging the immunoaffinity interactions between exosome surface proteins and their cognate antibodies. Here we describe the workflow of immuno magnetic isolation and analysis of exosomes by flow cytometry Western immunoblotting and electron microscopy. Owing to the features of magnetic beads exosomes can be easily processed via washing and elution steps and isolated with high purity and yield within 40 min.
1 Specific and Direct 2 Semi Generic and Direct and 3 Generic and Direct as well as exosome release from the magnetic beads. Here we describe the workflow of immuno magnetic isolation and analysis of exosomes by flow cytometry Western immunoblotting and electron microscopy. The red and blue bars represent the flow analysis pre- and post-exosome isolation for western blotting respectively.
Three direct exosome isolation strategies are described. Exosome-bound beads were washed and isolated via a magnetic feature. Magnetic bead-based isolation of exosomes.
Potential subpopulations of exosomes can be captured by targeting these markers using magnetic beads. A method for determining the ac-. Bead-based exosome isolation.
Present in all bodily fluids exosomes have been associated with cell sig-naling. C Exosomes were isolated for western blotting using anti-CD9 antibodycoated magnetic beads 25x the amount of beads used for flow cytometric analysis and the remaining supernatant was subjected to a second round of exosome capture for flow cytometric analysis as described above. Magnetic bead-based isolation of exosomes.
Next the exosome-bound beads were carefully washed to remove non-target proteins using a washing buffer 2 mL with pH 6 to resuspend the exosome captured beads. The magnetic bead-based isolation workflow is dramatically shortened both by omitting the pre-enrichment step and providing an option for a very short capture time. Researchers at the National Tsing Hua University Taiwan have designed a two-step magnetic bead-based 2MBB method for isolation a subset of EVs as well as their microRNAs from samples of a limited amount.
Also exosomes of tumor origin were isolated from tumor cells using antibodies against tumor-associated HER2 and EpCAM.
 Immunomagnetic Isolation Of Brain Derived Evs Using Tenpo A The Scientific Diagram
Immunomagnetic Isolation Of Brain Derived Evs Using Tenpo A The Scientific Diagram
 Cancers Full Text Micrornas From Liquid Biopsy Derived Extracellular Vesicles Recent Advances In Detection And Characterization Methods
Cancers Full Text Micrornas From Liquid Biopsy Derived Extracellular Vesicles Recent Advances In Detection And Characterization Methods
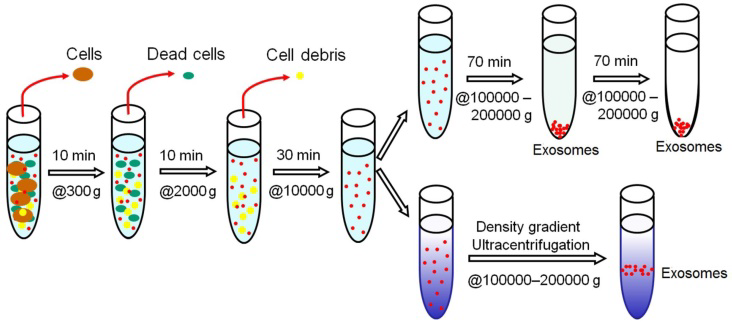 Exosome Isolation By Centrifugation Filtration Immunoaffinity More
Exosome Isolation By Centrifugation Filtration Immunoaffinity More
 Exosome Isolation And Analysis Miltenyi Biotec Sverige
Exosome Isolation And Analysis Miltenyi Biotec Sverige
 Methods And Technologies For Exosome Isolation And Characterization Zhang the ones Small Methods Wiley Library
Methods And Technologies For Exosome Isolation And Characterization Zhang the ones Small Methods Wiley Library
 Schematic View Of Different Microfluidic Based Exosome Isolation Scientific Diagram
Schematic View Of Different Microfluidic Based Exosome Isolation Scientific Diagram
 Comparison Of Isolation Methods Using Commercially Kits For Obtaining Extracellular Vesicles From Cow Milk Journal Of Dairy Science
Comparison Of Isolation Methods Using Commercially Kits For Obtaining Extracellular Vesicles From Cow Milk Journal Of Dairy Science
 Iba Fab Tacs Exosome Isolation Kit Sciencewerke
Iba Fab Tacs Exosome Isolation Kit Sciencewerke
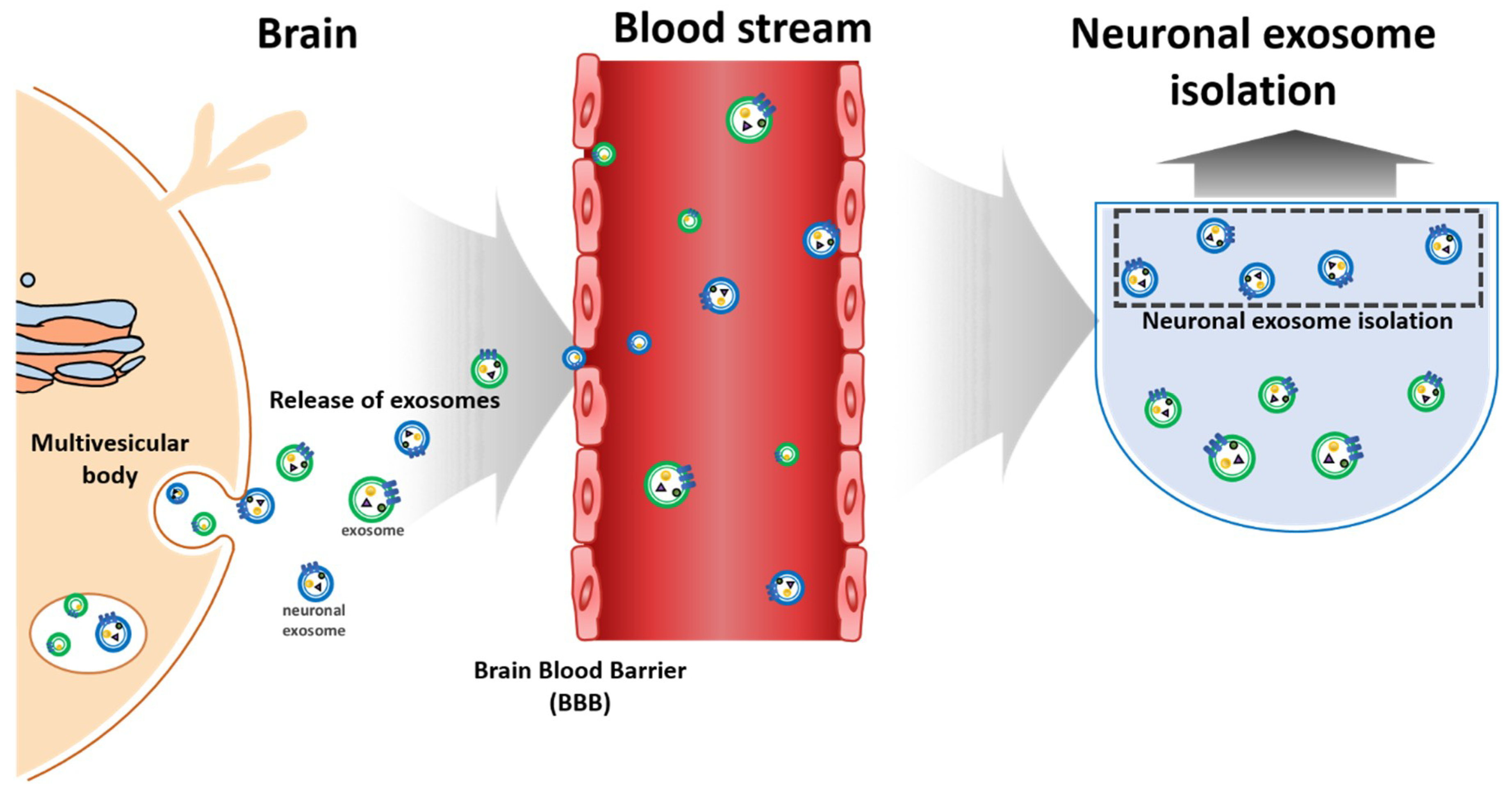 Micromachines Full Text Toward Exosome Based Neuronal Diagnostic Devices
Micromachines Full Text Toward Exosome Based Neuronal Diagnostic Devices
 Size Exclusion Chromatography Isolation Of Exosomes From Rat Blood Scientific Diagram
Size Exclusion Chromatography Isolation Of Exosomes From Rat Blood Scientific Diagram
 Dynabeads Cell Isolation And Expansion Support Getting Started Thermo Fisher Scientific Thermo Fisher Cell Isolation
Dynabeads Cell Isolation And Expansion Support Getting Started Thermo Fisher Scientific Thermo Fisher Cell Isolation
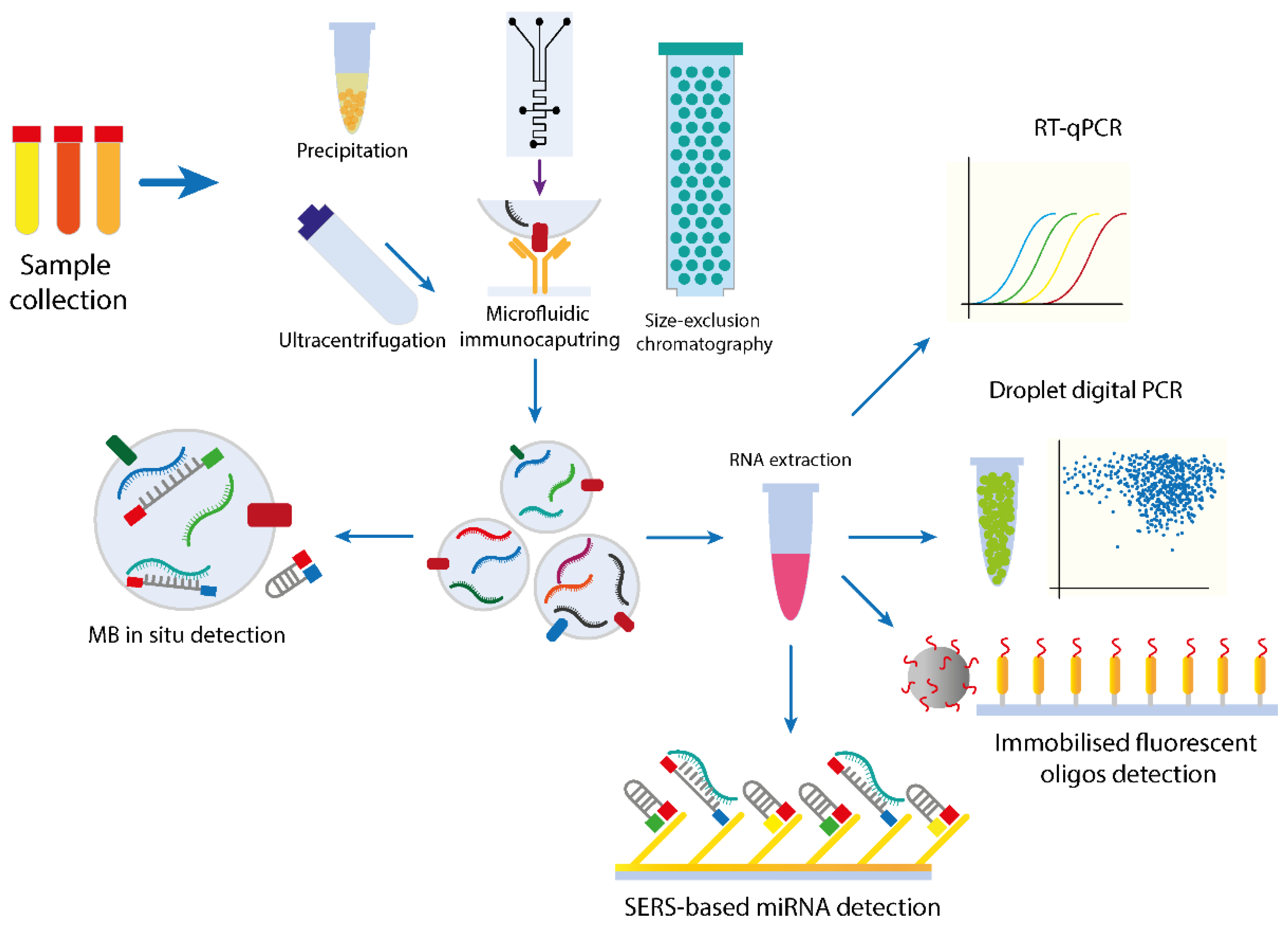 Cancers Full Text Micrornas From Liquid Biopsy Derived Extracellular Vesicles Recent Advances In Detection And Characterization Methods
Cancers Full Text Micrornas From Liquid Biopsy Derived Extracellular Vesicles Recent Advances In Detection And Characterization Methods
 Exosome Isolation And Analysis Miltenyi Biotec Sverige
Exosome Isolation And Analysis Miltenyi Biotec Sverige
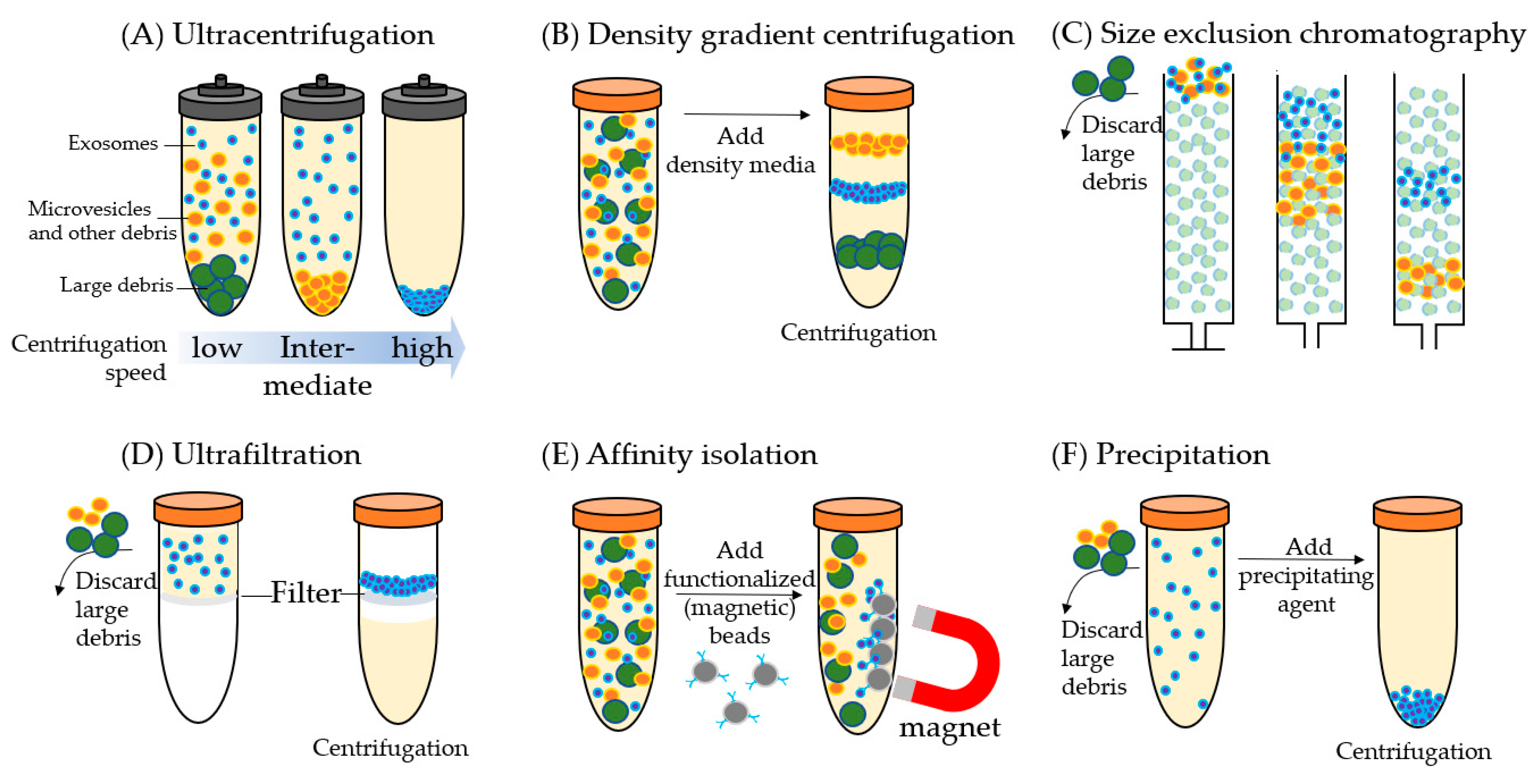 Cancers Full Text Proteomic Analysis Of Exosomes For Discovery Of Protein Biomarkers For Prostate And Bladder Cancer
Cancers Full Text Proteomic Analysis Of Exosomes For Discovery Of Protein Biomarkers For Prostate And Bladder Cancer
 Examples Of Microfluidic Approaches For Exosome Isolation In Plasma Scientific Diagram
Examples Of Microfluidic Approaches For Exosome Isolation In Plasma Scientific Diagram
 Schematic View And Comparison Of Conventional A E And Microfluidic Scientific Diagram
Schematic View And Comparison Of Conventional A E And Microfluidic Scientific Diagram
 Isolation Protocol And Characterization Of Extracellular Vesicles Scientific Diagram
Isolation Protocol And Characterization Of Extracellular Vesicles Scientific Diagram
 Conventional And Emerging Exosome Isolation Techniques Scientific Diagram
Conventional And Emerging Exosome Isolation Techniques Scientific Diagram
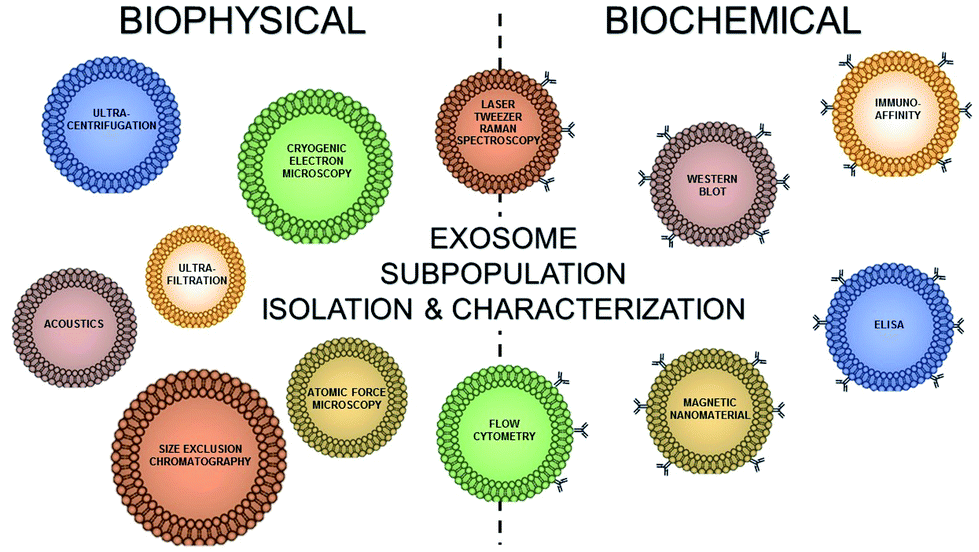 Separation Of Distinct Exosome Subpopulations Isolation And Characterization Approaches And Their Associated Challenges Analyst Rsc Publishing
Separation Of Distinct Exosome Subpopulations Isolation And Characterization Approaches And Their Associated Challenges Analyst Rsc Publishing
 Schematic Illustration Of Pll Clustering Method For Extracellular Scientific Diagram
Schematic Illustration Of Pll Clustering Method For Extracellular Scientific Diagram
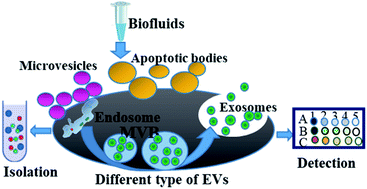
 Conventional And Emerging Exosome Isolation Techniques Scientific Diagram
Conventional And Emerging Exosome Isolation Techniques Scientific Diagram
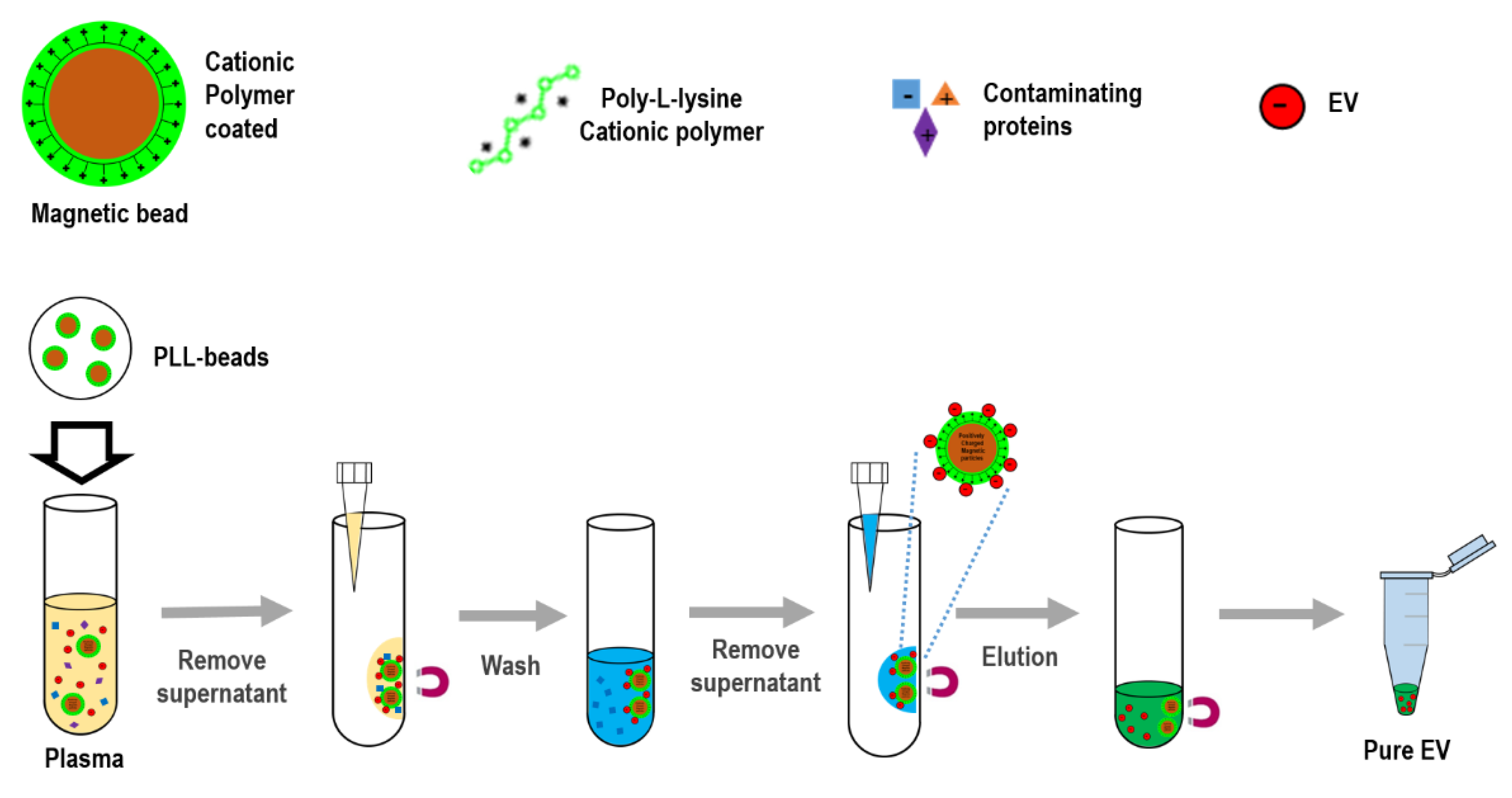 Biomedicines Full Text Exocas 2 Rapid And Pure Isolation Of Exosomes By Anionic Exchange Using Magnetic Beads
Biomedicines Full Text Exocas 2 Rapid And Pure Isolation Of Exosomes By Anionic Exchange Using Magnetic Beads